Pathways
Pathways are the means and routes by which invasive species are introduced into new environments. Pathways can generally be classified as either natural or man-made.
Natural pathways (self introduction on their own) include wind, currents (including marine debris), and other forms of natural dispersal that can bring species to a new habitat.
Man-made (human assistance) pathways are those which are created or enhanced by human activity. These are characteristically of two types:
- Intentional, which is the result of a deliberate movement of a species by humans outside of its natural range. Examples include the introduction of biological control organisms or the movement of species for the horticultural or pet trade. Intentional introductions as a whole should not be labeled as either good or bad. A specific intentional pathway can only be judged by the positive or negative impact of the specific organisms that are moving along that means.
- Unintentional,which is the inadvertent or accidental movement of species as a byproduct of some other human activity. Examples of unintentional pathways are ballast water discharge (e.g. red-tide organisms), pests and diseases in imported plants, firewood, and other agricultural products (e.g. fire ants), the movement of recreational watercraft (e.g. zebra mussels), and the international movement of people (e.g. pathogens). In these and countless other unintentional pathways, the movement of non-native species is an indirect byproduct of human activities.
For our purposes, the term "vector" is viewed as a biological pathway for a disease or parasite (i.e. an organism that transmits pathogens to various hosts) and is not completely synonymous with the much broader definition of a pathway. The Asian citrus psyllid is an example of a vector of the serious citrus greening disease or Huanglongbing.
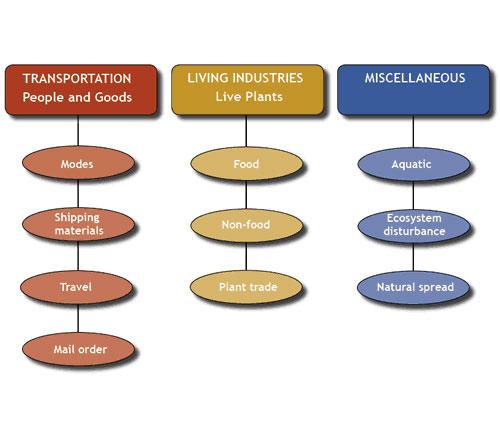
Examples of How Invasive Species are Spread
- Agricultural materials (see related resource: Hungry Pests - How They Spread)
- Aquaculture farming (see Western Aquatic Invasive Species Resource Center - Aquaculture)
- Aquarium trade (see Zebra Mussels Found in Aquarium Moss Balls / Western Aquatic Invasive Species Resource Center - Aquarium Trade)
- Ballast water and shipping (see Clear Seas - Invasive Species & Marine Shipping)
- Classroom or science lab; escapes or introductions (see Habitttitude - Classroom Education)
- Firewood (see related resource: Hungry Pests - How They Spread)
- Firefighting equipment (see Western Aquatic Invasive Species Resource Center - Firefighting Equipment) and Other equipment (see Western Aquatic Invasive Species Resource Center - Other Equipment)
- Fishing gear and bait (see Western Aquatic Invasive Species Resource Center - Bait)
- Food trade and its packing material (See USGS - Survey and Assessment of Live Food Markets as an Invasion Pathway)
- Fouled hulls of commercial and recreational vessels; boats (Northeast Marine Introduced Species - Pathways and Prevention: Shipping)
- Internet sales (see related resource: Hungry Pests - How They Spread)
- Mail (see related resource: Hungry Pests - How They Spread)
- Marine debris (see Western Aquatic Invasive Species Resource Center - Marine Debris)
- Moving (see related resource: Hungry Pests - How They Spread)
- Ornamental nonnative plant sales (see Invasive Plants are Still for Sale as Garden Ornamentals, Research Shows)
- Outdoor gear; hitchhikers on boots, clothes, and camping equipment (see related resource: Hungry Pests - How They Spread)
- Passenger baggage (see related resource: Hungry Pests - How They Spread)
- Pets; unwanted or escaped and exotic vertebrates (see Don't Let It Loose)
- Plants and plant parts; escaped or disposals (see related resource: Hungry Pests - How They Spread)
- Recreational vehicles (RVs) (see related resource: Hungry Pests - How They Spread)
- Remote Operated Vehicles (ROVs) (see Western Aquatic Invasive Species Resource Center - ROVs)
- Seaplanes (see Western Aquatic Invasive Species Resource Center - Seaplanes)
- SCUBA gear (see Western Aquatic Invasive Species Resource Center - SCUBA)
- Watercraft (see Western Aquatic Invasive Species Resource Center - Watercraft)
- Water gardening (see Western Aquatic Invasive Species Resource Center - Water Gardening)
Spotlights
All Resources
Selected Resources
The section below contains highly relevant resources for this subject, organized by source.
